Role of digital workers to jump by 50%:IDC
The role of digital workers within organisations is expected to increase by 50% over the next two years as human-machine collaboration becomes more mainstream. This is according to research company IDC, which has surveyed 500 senior decision-makers in large enterprises for the White Paper, Content Intelligence for the Future of Work, sponsored by ABBYY.
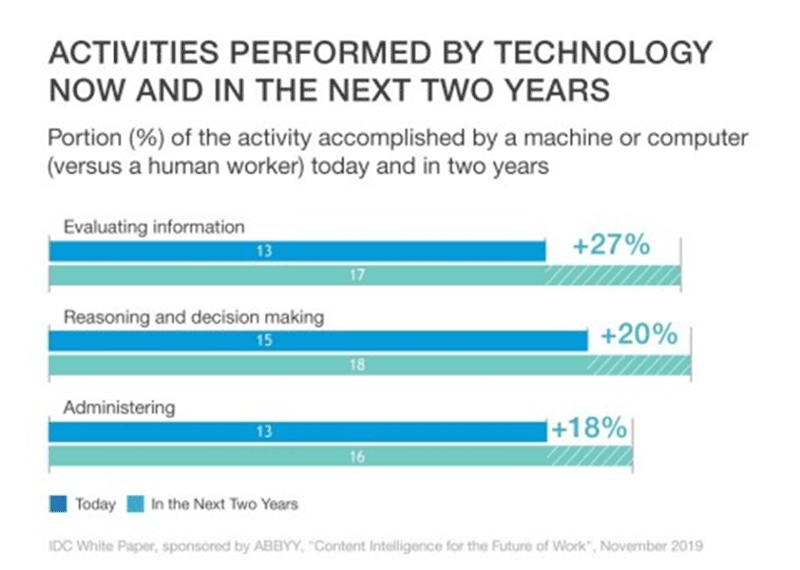
It is not just mundane, repetitive jobs like data input that new digital colleagues will help human workers complete in the years ahead. The growth of machine learning (ML) through human-centric artificial intelligence (AI) means robot assistants will also help employees make better decisions. In most cases, these technologies enhance rather than replace human capabilities. For example, the survey found that technology evaluating information will grow by 28% in two years, and 18% of activities related to reasoning and decision making will be performed by machines.
IDC defines a “digital worker” as technology - including artificial intelligence (AI), intelligent process automation (IPA), augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR), and software robotics – tha tautomates and augments work previously accomplished by humans.
Holly Muscolino, research vice president of content and process strategies and the future of work at IDC believes that this will soon become the “new normal” for many businesses:
“A growing number of employees will find themselves working side-by-side with a digital coworker in the future as technology automates many work activities. Think human and machine. The human-machine collaboration is not just the future of work, but it is the new normal for today’s high-performing enterprises.”
IDC predicts that the intelligent process automation (IPA) software market, which includes robotic process automation (RPA), will grow from $13.1bn in 2019 to $20.7bn in 2023, with businesses expecting to increase spending on content intelligence technologies over the next year by an average of 31%.
When survey respondents were asked about the factors that drove them to deploy (or plan to deploy) content intelligence technologies, they indicated manual sorting and classification of documents, manual data extraction from documents, inadequate compliance with security/privacy regulations, and poor data, errors, and inaccuracy of information as top pain points.
Over 40% of survey respondents have experienced a notable increase in customer satisfaction and employee productivity by deploying content intelligence technologies into their digital transformation strategy. Additionally, more than 1/3 of respondents saw an improvement in responsiveness to customers, new product or revenue opportunities, increased visibility and/or accountability, or increased customer engagement.
“The IDC survey proves that automation can and should be human-centric, augmented with artificial intelligence,” said Bruce Orcutt, Senior Vice President of Product Marketing at ABBYY. “Ethical, responsible automation will create a more productive, happier future where human workers can focus on higher-level, creative and socially responsible tasks, and customers get better experiences with faster service. Businesses that are early-adopters of incorporating content intelligence within their automation platforms will gain a significant competitive edge.”
Other key findings:
- 75% of respondents said their organization was finding it difficult to recruit digital skills
- Over 20% cited inadequate worker skills and/or training
- The top three corporate initiatives enabled by content intelligence are employee engagement, customer engagement and digital transformation
The IDC White Paper “Content Intelligence for the Future of Work” is available at https://www.abbyy.com/en-eu/solutions/content-iq/content-intelligence-for-the-future-of-work/.
