Is Capture on Collision Course With Rpa?
A new Report from analysis and consulting firm Infosource Software examines the overlap between the traditional Capture market, as well as a subset of the Robotic Process Automation (RPA) market that includes Capture-type applications. Both offer solutions for the automated ingestion and processing of business inputs.
The IDP (Intelligent Document Processing) market sits at the intersection of the traditional Intelligent Capture Market and the RPA market.
Key overlapping use cases include Invoice Processing and Case Management applications like onboarding and claims management. Both present growing opportunities for traditional Capture Software solutions. RPA vendors are also targeting these use cases but are often lacking Capture capabilities for more complex unstructured documents.
Over the last few years. Capture vendors have expanded their portfolios through acquisitions of RPA startups and partnerships with major RPA vendors. Conversely RPA vendors have a requirement to augment their capabilities related to unstructured data extraction; this can be accomplished through partnerships, acquisitions, or development of their own Capture technology.
Market Ecosystem and Segment Definitions
Infosource defines Capture as software and solutions that automate the ingestion of information into business processes.
Traditional Capture software is developed around the ingestion and processing of unstructured or semi-structured business inputs with the objective to automate business processes. It acquires, classifies, and converts multi-channel business inputs into usable data for business transactions, analytics, records management, discovery, and compliance applications.
RPA software combines solutions and services used to automate mundane and repetitive business tasks or entire processes with the objective to replace human keystrokes. Part of these solutions automate processes that include the ingestion of business information, hence are considered Capture related.
While Traditional Capture Software solutions and Capture-related RPA solutions both aim to automate information intensive processes, they differ materially in their focus and technology applied.
|
|
Traditional Capture Software |
|
|
Primary objective |
Capture Software is developed around ingestion, invoking solutions, and services used to process business inputs. |
|
| Capture-related RPA Software | ||
| Primary objective | RPA Software combines solutions and services used to automate repetitive business processes; it replaces human keystrokes. | |
| Traditional Capture Software | ||
|
Structured vs. unstructured information |
Capture Software understands and extracts meaningful, accurate, and usable information from unstructured business inputs. |
|
| Capture-related RPA Software | ||
| Structured vs. unstructured information | Traditional RPA Software extracts and consolidates structured information from files and systems required for a business process. IDP solutions extract and process unstructured and semi-structured business inputs. | |
| Traditional Capture Software | ||
|
Data extraction and processing |
Capture Software acquires, classifies, and converts unstructured and semi-structured information into enhanced usable business information. It uses Capture technologies including the enhancement of images, the recognition of machine and handwriting, classification of inputs, extraction, validation, and enhancement of extracted data. |
|
| Capture-related RPA Software | ||
| Data extraction and processing | RPA Software often offers basic OCR capabilities for extracting structured data. For business use cases that involve unstructured and semi-structured information it relies on Capture technology to extract the relevant inputs required for the business process. |
A subset of these Capture-related RPA solutions addresses use cases involving unstructured and semi-structured inputs, mostly document based, which are referred to as Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solutions. These present the direct intersection between the Traditional Capture market and the Capture-related RPA market, as the respective solutions address use cases that involve the extraction and processing of unstructured and semi-structured business inputs, e.g., invoice processing, customer onboarding, and claims processing.

Convergence of the Traditional Capture and the RPA Market
Other Capture-related RPA use cases include Sales and Marketing support, most frequently Contact Centre applications, which intersect with the adjacent Customer Experience Management (CEM) market.
Capture and RPA Use Cases
The primary use cases for traditional Capture Software applications overlap with those of IDP solutions.
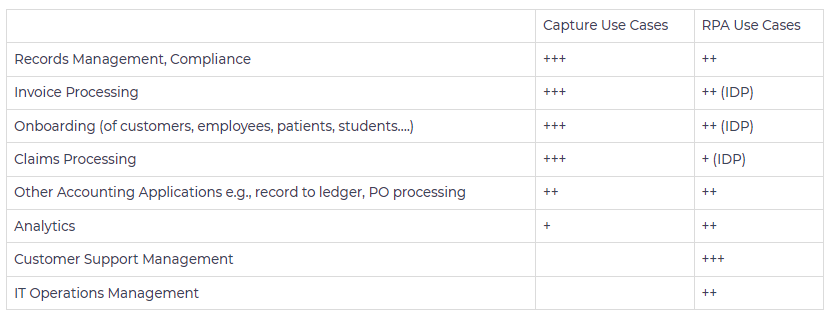
In the traditional Capture Software market, Records Management was the primary reason for Capture in the first decades, when business inputs were received and stored in paper format and needed to be digitized. This use case continues to be important to comply with rules and legislations. It also includes smaller use cases related to analytics and discovery. Those also present a relevant but smaller use case for RPA, mostly focused on compiling data from multiple repositories in preparation for compliance-driven reporting and analytics.
In the last decade, Accounting became the major use case for traditional Capture applications in transactional processing, as recognition technology improved to cover semi-structured documents, such as invoices, and was able to fulfil the need to automate the Account Payable process, in particular for enterprises with large volumes of incoming invoices. Intelligent Capture has evolved to handle nested tables that are common for line-item extraction across A/P and A/R documents. Demand has been expanding to mid-sized companies. RPA vendors with IDP capabilities are increasingly addressing this use case.
In the last few years, there has been increased focus on customer experience. This has driven a demand for Case Management use cases in the traditional Capture software market and the demand for Capture-related RPA solutions. These include solutions for automating customer / patient / employee onboarding and claims / mortgage applications.
In addition to IDP-type solutions, which overlap with the traditional Capture, RPA use cases include customer support applications, internal workflow automation like IT Operations Management, and ITSM- and reporting-focused use cases, e.g., journal entries and other applications that involve the automated extraction of data from websites or legacy systems which replace manual data entry.
In 2020, the two major application groups in the traditional Capture market were Accounting and Case Management, representing 33% and 34% of the global market value. In the Capture-related RPA market, IDP applications, which target the same use cases, accounted for over half of the end customer market. Case Management applications represent the largest IDP application. Customer experience management (CEM) related applications account for almost a quarter of the Capture-related RPA market segment.
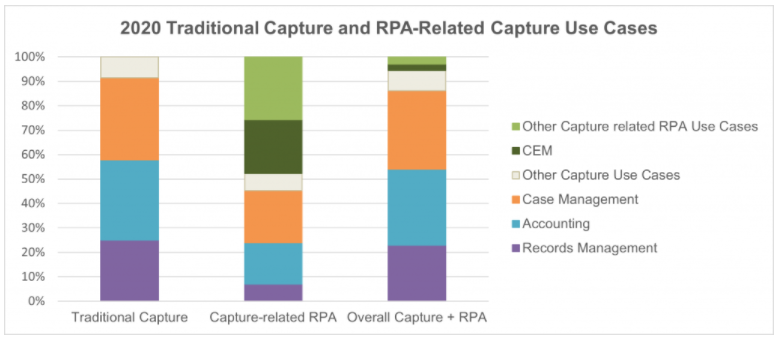
Infosource expects Capture-related RPA use cases to shift more towards IDP-type solutions over the next few years. This means that they will increasingly target use cases also covered by traditional Capture solutions, hence these two markets will increasingly converge.
In the traditional Capture Software market, the Finance sector (consisting of Banking and Insurance) and the Public sector (consisting of Central and State & local Government) account for the largest verticals followed by Healthcare and Manufacturing.
In the RPA market, the Banking sector, which offered some early use cases for RPA solutions, is the largest vertical for Capture-related RPA solutions as legacy systems continue to present a hurdle for process automation. Telecommunications and Utilities are the second major industry group in the RPA segment. Both verticals are highly competitive and therefore under significant pressure to streamline processes and enhance customer service. Manufacturing and Healthcare represent the second tier of verticals. Target use cases include invoice processing for Manufacturing and onboarding for Healthcare, both overlapping with traditional Capture use cases.
Market Size and Growth in 2020
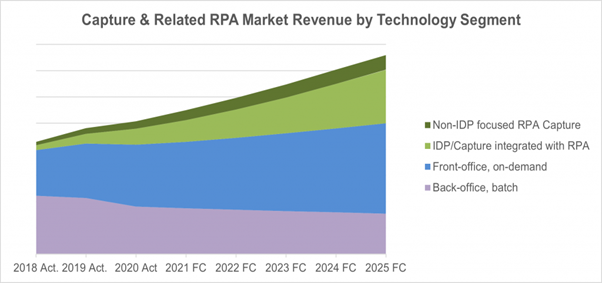
The global Capture market that combines traditional Capture Software solutions and Capture-related RPA solutions exceeded USD 5 billion of end customer level revenue in 2020. The vast majority of these solutions, USD 4.5 billion, is offered by Capture Software vendors. They include a small element of RPA solutions that they added through acquisitions, as well as a subsegment of “Capture to RPA” solutions.
Starting in 2016, Capture-related RPA solutions emerged and drove part of the growth of the overall Capture market in 2018 and 2019. During 2020, where the growth of the traditional Capture market was significantly slowed due to the pandemic, the RPA market overall, including the Capture-related RPA solutions, grew by 58% YOY.
In 2020, the traditional Capture software market, which includes back-office/batch applications, front-office/on demand implementations, and traditional Capture sold as the front-end of RPA, was almost flat, after growing in high single digital for the previous three years. It was tempered by declining sales for back-office/batch Capture, as on-site implementations were put on hold during the pandemic. There was growth in front-office on-demand Capture software sales, which was implemented with the purpose of collecting input from distributed and remote sites.

Predicted Development
The strong demand for RPA solutions is expected to continue, including Capture-related RPA offerings. These solutions will overlap and compete with traditional Intelligent Capture solutions for the same use cases. They will likely be fulfilled by Capture vendors through expanded portfolios or RPA vendors providing IDP-type offerings or leveraging partnerships with Capture vendors. We expect solutions involving RPA technology to drive most of the growth in the coming years. By 2025, the combined Capture integrated with RPA and IDP segments are predicted to make up more than a quarter of the market.
The Future of the Market = Capture + RPA
Over the last couple of years, Capture Software vendors have acquired RPA technology to expand their capabilities. Examples from 2020 are: IBM acquired the Brazilian company WDG; Hyland acquired the German firm “Another Monday”; and Microsoft acquired UK headquartered RPA vendor Softomotive.
RPA vendors have targeted the Capture market as they look to expand their capabilities to be able to ingest unstructured data into their process automation applications. To address this, they began partnering with traditional Capture vendors. ISVs like ABBYY, Ephesoft, and Hyperscience were some of the first to have success through RPA partnerships.
In 2017, Automation Anywhere, one of the big three in the RPA market, introduced IQ Bot, its own Capture application. Recently, UiPath and Blue Prism have followed suit. We have also seen a number of IDP applications introduced by smaller RPA players, many of which have roots in the service bureau space.
There continues to be an opportunity for partnerships and acquisitions between RPA and Capture vendors – for RPA vendors to augment their capabilities related to data extraction and conversely for Capture Software vendors to partner with RPA vendors to expand their automation capabilities.
To purchase the complete report, contact Craig Laue, Head of Strategic Sales, at cl@info-source.com or +1 408-726-4550.
